Seagram Building
Contents |
[edit] Introduction
The Seagram Building is an iconic skyscraper located on Park Avenue in mid-town Manhattan, New York City. It was designed by architect Ludwig Mies van der Rohe in the International Style, which would influence the architectural style of New York’s skyscrapers for several decades.
Characterised by sleek glass and metal, rather than the ornamental heavy stone and brick facades of previous decades, the Seagram Building signalled a new era of functional skyscraper, adopting a minimalist, corporate aesthetic.
The building stands 157 m (515 ft) tall, with 38 storeys and was completed in 1958. It was originally designed as the headquarters for Joseph E. Seagram’s & Sons, and was Mies’ first tall office building project.
Today, it is owned by RFR Holdings and remains a prominent example of mid-century modernist architecture. However, it also has an Energy Star rating of 3 out of 100, the worst of any New York building.
[edit] Architectural design
[edit] Structure
One of the key traits of the International style was to articulate the structure of the building externally, rather than concealing it under applied ornamentation.
The Seagram Building was built using a combination of a steel moment frame and a steel and reinforced concrete core for lateral stiffness, one of the first buildings of its kind to do so. The structural engineering consultants, Severud Associates, claimed it was the first tall building to use high-strength bolted connections, and the first to combine a braced with a moment frame. In addition, it was one of the first buildings of its kind to use a vertical truss bracing system.
Mies had intended for the steel frame to be visible, however, this was prevented by the American building codes which required the covering of all structural steel with concrete or another fire-resistant material. To give the building the vertical articulation he wanted, Mies used non-structural bronze-toned I-beams instead, which run vertically (in the same way as mullions), surrounding the large glass windows, also helping to stiffen the skin for wind loading. This method of a larger non-structural edifice being supported by an interior reinforced concrete shell would go on to be widely adopted for other buildings.
[edit] Window blinds
A characteristic of the International style is the building’s uniform appearance. To avoid the undesirable, disordered irregularity of window blinds being drawn to different lengths, Mies specified blinds which were operationally limited to three positions – fully open, halfway open, or fully closed.
[edit] Interior
It was the use of expensive, high-spec materials and lavish decoration in the interiors which made the Seagram Building the world’s most expensive skyscraper at the time of its completion. The building used 1,500 tons of bronze, in addition to travertine and marble. This was intended to provide cohesion with the sleek, yet minimalist, external aesthetic.
[edit] Plaza
Another pioneering feature of the design was Mies’ decision to set the building back 100 ft from the edge of the street, creating an open plaza. This was part of his response to the dense environment of Manhattan, and was a rebuke to the conventional economics of skyscraper design and urban planning.
The plaza incorporates two large fountains and outdoor seating, encouraging the socialisation of the space, and providing a 'threshold' linking the city with the building.
Such plazas have now become something of an architectural cliché, but at the time it was celebrated as being innovative and unique.
[edit] Related articles on Designing Buildings Wiki
Featured articles and news
A case study and a warning to would-be developers
Creating four dwellings... after half a century of doing this job, why, oh why, is it so difficult?
Reform of the fire engineering profession
Fire Engineers Advisory Panel: Authoritative Statement, reactions and next steps.
Restoration and renewal of the Palace of Westminster
A complex project of cultural significance from full decant to EMI, opportunities and a potential a way forward.
Apprenticeships and the responsibility we share
Perspectives from the CIOB President as National Apprentice Week comes to a close.
The first line of defence against rain, wind and snow.
Building Safety recap January, 2026
What we missed at the end of last year, and at the start of this...
National Apprenticeship Week 2026, 9-15 Feb
Shining a light on the positive impacts for businesses, their apprentices and the wider economy alike.
Applications and benefits of acoustic flooring
From commercial to retail.
From solid to sprung and ribbed to raised.
Strengthening industry collaboration in Hong Kong
Hong Kong Institute of Construction and The Chartered Institute of Building sign Memorandum of Understanding.
A detailed description from the experts at Cornish Lime.
IHBC planning for growth with corporate plan development
Grow with the Institute by volunteering and CP25 consultation.
Connecting ambition and action for designers and specifiers.
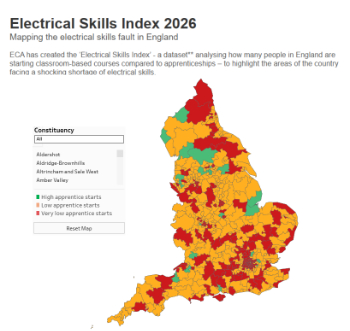
Electrical skills gap deepens as apprenticeship starts fall despite surging demand says ECA.
Built environment bodies deepen joint action on EDI
B.E.Inclusive initiative agree next phase of joint equity, diversity and inclusion (EDI) action plan.
Recognising culture as key to sustainable economic growth
Creative UK Provocation paper: Culture as Growth Infrastructure.